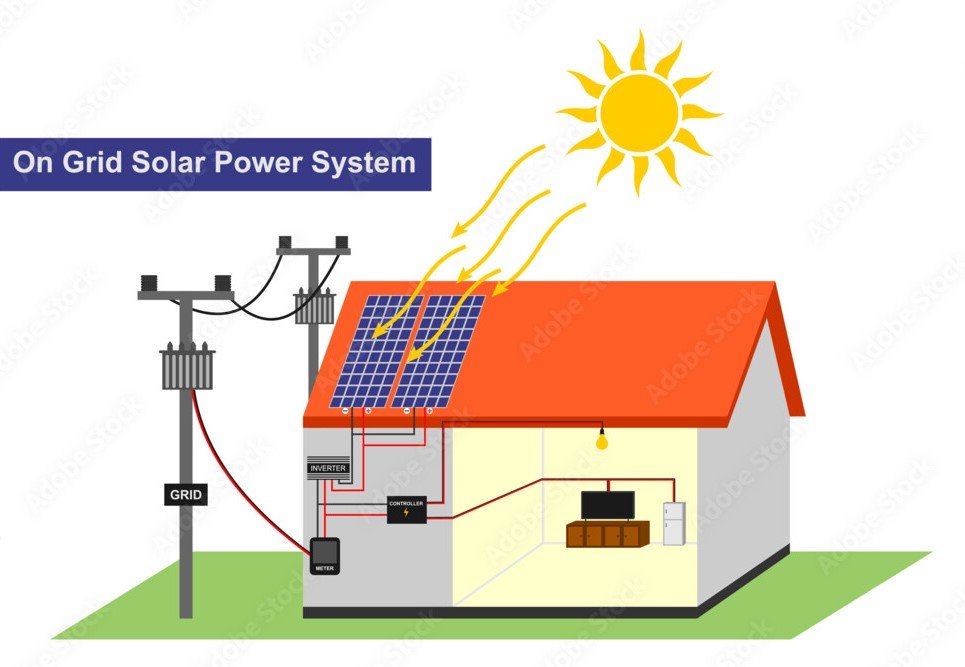
On-Grid Solar System
Photovoltaic (PV) systems are generally divided into two major categories: grid-connected (also known as grid-tied) systems that are interfaced to an electricity grid and stand-alone systems that are self-contained. Since the 1990s, the market has shifted decisively toward PV power plants and installations on buildings connected to an electricity grid. In 2000, grid-connected PV had overtaken stand-alone systems in global market share, and in 2016, more than 98% of solar cell production was being deployed in grid-connected systems.
Benefits
- Cost-Effective: On-grid systems are generally less expensive to install compared to off-grid systems because they don't require battery storage.
- Lower Electricity Bills: By generating your own electricity and participating in net metering, you can significantly reduce your utility bills.
- Environmental Impact: On-grid solar systems contribute to a reduction in carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels by harnessing renewable solar energy.
- Easy Maintenance: These systems typically require less maintenance than off-grid systems since there are no batteries to replace.
Limitations
- Dependency on Grid: If there is a power outage, on-grid systems will not provide electricity unless there is a battery backup, as they are designed to shut down for safety.
- Initial Investment: While costs have decreased, the initial investment can still be significant, although it may be offset by savings over time.
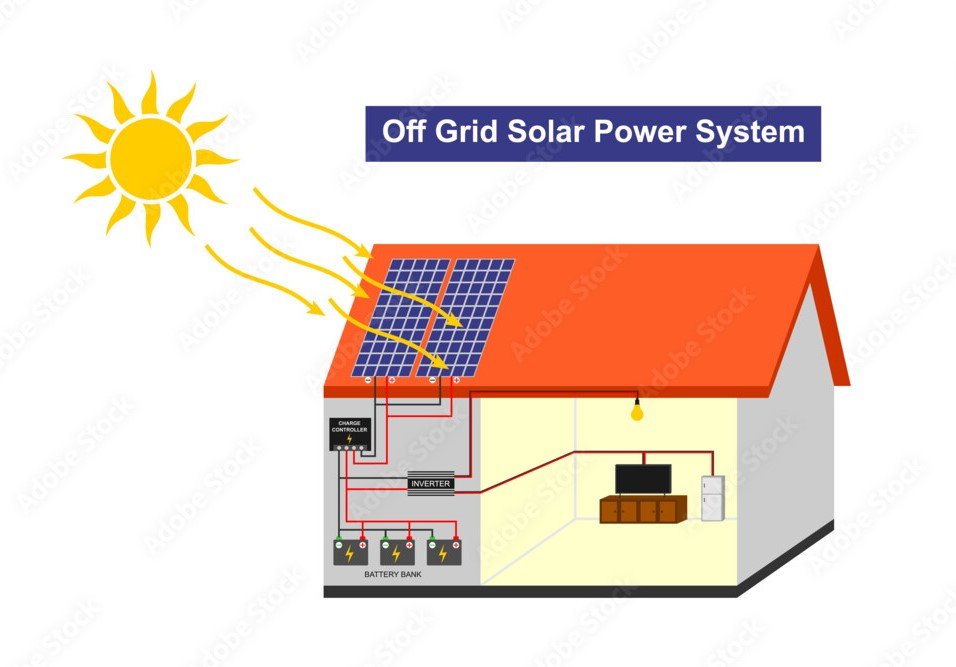
Off-Grid Solar System
A solar system with battery storage and a backup is called an off-grid solar system that generates electricity after a power cut or during the night hours. It has four major components, solar panels, inverter, battery and balancing of system. This solar system is more popular and comes with a power backup and it works independently of the grid.
Benefits
- Independence: Off-grid systems provide complete energy independence from the utility grid, making them ideal for remote areas or locations prone to power outages.
- Sustainability: They harness renewable energy from the sun, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a decrease in carbon emissions.
- Energy Security: With a reliable power supply, users are less affected by fluctuations in energy prices or grid failures.
- Customizable: Off-grid systems can be tailored to meet specific energy needs, allowing for various configurations and battery capacities based on consumption patterns.
- Self-Sufficiency: Users can become self-sufficient in terms of energy production and consumption, which can be empowering for many individuals and communities
Limitations
- Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment for off-grid systems can be significantly higher due to the cost of batteries and additional equipment, such as charge controllers and backup generators.
- Maintenance: Battery systems require regular maintenance and eventual replacement, which can add to the overall cost and complexity of the system.
- Limited Power Supply: The amount of energy available is dependent on solar production and battery capacity. Users must manage their energy consumption, especially during periods of low sunlight.
- Space Requirements: Off-grid systems may require more space for battery storage, especially if larger batteries are needed to meet energy demands.

Hybrid Solar System
Hybrid solar systems produce usable electricity with the help of hybrid solar inverters and batteries. The power stored in the batteries can be used later on. These Hybrid solar systems work in the same manner as traditional grid-tied solar systems. But since they can also store energy, most hybrid systems can function as a backup power source too.
Benefits
- Energy Independence: By combining solar energy generation and battery storage, hybrid systems provide a level of energy independence from the grid, ensuring power availability even during outages.
- Cost Savings: Users can save on electricity bills by using solar power and battery-stored energy during peak rate times. Excess energy can be sold back to the grid, further reducing costs.
- Reliability: Hybrid systems provide a consistent power supply by utilizing solar energy when available and seamlessly switching to grid electricity or battery power as needed.
- Environmental Impact: By utilizing renewable solar energy, hybrid systems help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
- Scalability: Hybrid systems can be easily expanded by adding more solar panels or batteries, allowing users to adjust their energy capacity based on changing needs
Limitations
- Higher Initial Investment: The upfront costs for hybrid systems can be higher than traditional on-grid systems due to the additional components like batteries and advanced inverters.
- Battery Maintenance: While hybrid systems offer battery storage, batteries require maintenance and eventual replacement, which can incur additional costs..
- Complexity: The integration of multiple components can make hybrid systems more complex to install and manage compared to simpler on-grid or off-grid systems.